Data Exploration
Time period
We are majorly interested in the time period “2019-02-01” ~ “2019-04-30” and “2020-02-01” ~ “2020-04-30”, where the second period is when China entered mass lockdown to control the spread of COVID-19. We used multiple strategies to visualize that, how the air quality index of different pollutants during the lockdown changed comparing to the same period in 2019, in major Chinese cities.
Besides the above time periods, we also extracted air quality data of each city from 2018 and 2021 to get a more comprehensive view of change in air quality in Chinese cities.
period_18 = interval(ymd("2018-02-01"), ymd("2018-04-30"))
period_19 = interval(ymd("2019-02-01"), ymd("2019-04-30"))
period_20 = interval(ymd("2020-02-01"), ymd("2020-04-30"))
period_21 = interval(ymd("2021-02-01"), ymd("2021-04-30"))Air quality data
Get the filenames of the air quality data.
city_files = list.files("30_cities_data")
onehundrd_city_files = list.files("100_cities_data")city_period_diff will hold each city’s mean daily AQI difference of each pollutant, between 2019 Feb~Apr and 2020 Feb~Apr.
city_period_diff =
tibble(city = character(),
pm25 = numeric(),
pm10 = numeric(),
o3 = numeric(),
no2 = numeric(),
so2 = numeric(),
co = numeric(),
)Daily Mean AQI difference Analysis
Compute the daily mean pollutant AQI from Feb to Apr of year 2019 and year 2020 in each city.
for (city_file in city_files) {
#print(city_file)
path = str_c("30_cities_data/", city_file)
city = strsplit(city_file, split = '-')[[1]][1]
cityAir = read_csv(path) %>%
mutate(date = as.Date(date, "%Y/%m/%d")) %>%
arrange(date)
cityAir_19 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_19)
cityAir_20 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_20)
pm25_19 = mean(cityAir_19$pm25, na.rm = T)
pm25_20 = mean(cityAir_20$pm25, na.rm = T)
pm25d = pm25_20 - pm25_19
pm10_19 = mean(cityAir_19$pm10, na.rm = T)
pm10_20 = mean(cityAir_20$pm10, na.rm = T)
pm10d = pm10_20 - pm10_19
o3_19 = mean(cityAir_19$o3, na.rm = T)
o3_20 = mean(cityAir_20$o3, na.rm = T)
o3d = o3_20 - o3_19
no2_19 = mean(cityAir_19$no2, na.rm = T)
no2_20 = mean(cityAir_20$no2, na.rm = T)
no2d = no2_20 - no2_19
so2_19 = mean(cityAir_19$so2, na.rm = T)
so2_20 = mean(cityAir_20$so2, na.rm = T)
so2d = so2_20 - so2_19
co_19 = mean(cityAir_19$co, na.rm = T)
co_20 = mean(cityAir_20$co, na.rm = T)
cod = co_20 - co_19
city_period_diff =
city_period_diff %>%
add_row(city = city,
pm25 = pm25d,
pm10 = pm10d,
o3 = o3d,
no2 = no2d,
so2 = so2d,
co = cod)
}city_period_diff =
city_period_diff %>%
mutate(
city = paste(
toupper(substring(city, 1, 1)),
substring(city, 2),
sep = ""),
city = fct_reorder(city, pm25, .desc = T),
)Interative bar graph of AQI Difference
city_period_diff %>%
plot_ly(x = ~pm25, y = ~city, type = "bar", opacity = 1) %>%
layout(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean PM25 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019",
barmode = 'overlay',
xaxis = list(title = "Mean AQI Difference"),
yaxis = list(autotick = F, title = "Cities"),
updatemenus = list(
list(
y = 1.1,
buttons = list(
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~pm25)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean PM25 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "pm25"),
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~pm10)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean PM10 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "pm10"),
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~o3)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean O3 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "o3"),
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~no2)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean NO2 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "no2"),
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~so2)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean SO2 AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "so2"),
list(method = "update",
args = list(list(x = list(~co)),
list(title = "Feb~Apr Daily Mean CO AQI Difference, 2020 minus 2019")
),
label = "co")
)
)))This interactive plot shows each pollutant’s Daily AQI difference, the value from 2020 Feb-Apr minus the value from 2019 Feb~Apr, in each city. A negative AQI change here indicates improvements in air quality. The users can click on the dropdown selection button on the top left to choose the pollutant type: PM2.5, PM10, O3, NO2, SO2 and CO. For PM2.5,PM10, CO and NO2, the mean AQI for most cities droped during the lockdown, showing general improvements in air quality. While for SO2 and O3, there are more cities with increased AQI during lockdown, with the O3 level increased for most of the cities in China..
Distribution Analysis
Now we will see how the distribution of daily PM25 AQI differ between time period 2019 Feb-Apr and 2020 Feb~Apr.
city_AQI_Distribution = tibble()
for (city_file in city_files) {
path = str_c("30_cities_data/", city_file)
city = strsplit(city_file, split = '-')[[1]][1]
cityAir = read_csv(path) %>%
mutate(date = as.Date(date, "%Y/%m/%d")) %>%
arrange(date)
city_19 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_19) %>%
mutate(period = "2019Feb-Apr",
day = format(date,"%m-%d"),
city = city) %>%
relocate(city, period, day)
#add a fake date "2019-02-29" with all AQI values as NA
city_19 =
city_19 %>%
add_row(city = city,
period = "2019Feb-Apr",
day = "02-29") %>%
mutate(day = as.factor(day))
city_20 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_20) %>%
mutate(period = "2020Feb-Apr",
day = format(date,"%m-%d"),
day = as.factor(day),
city = city) %>%
relocate(city, period, day)
city_AQI_Distribution = rbind(city_AQI_Distribution, city_19)
city_AQI_Distribution = rbind(city_AQI_Distribution, city_20)
}city_AQI_Distribution =
city_AQI_Distribution %>%
mutate(period = factor(period, levels = c("2020Feb-Apr", "2019Feb-Apr")),
city = paste(
toupper(substring(city, 1, 1)),
substring(city, 2),
sep = ""))Interactive Side-by-side Boxplots
#This way is stupid but it works! I tried other methods but they just don't work as expected!!!
city_AQI_Distribution %>%
plot_ly(
y = ~city, x = ~pm25, color = ~period, type = "box",
colors = c(rgb(0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 0.6), rgb(0.8, 0.2, 0.2, 0.6))) %>%
add_trace(
x = ~pm10, visible = F) %>%
add_trace(
x = ~o3, visible = F) %>%
add_trace(
x = ~no2, visible = F) %>%
add_trace(
x = ~so2, visible = F) %>%
add_trace(
x = ~co, visible = F) %>%
layout(title = "Daily PM25 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr",
xaxis = list(title = "Daily AQI"),
yaxis = list(autotick = F, title = "Cities"),
boxmode = "group",
updatemenus = list(
list(
y = 1.1,
buttons = list(
list(label = "PM25",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(T,T, F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F)),
list(title = "Daily PM25 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr"))),
list(label = "PM10",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(F,F, T,T, F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F)),
list(title = "Daily PM10 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr"))),
list(label = "O3",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(F,F, F,F, T,T, F,F, F,F, F,F)),
list(title = "Daily O3 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr"))),
list(label = "no2",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(F,F, F,F, F,F, T,T, F,F, F,F)),
list(title = "Daily NO2 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr"))),
list(label = "so2",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F, T,T, F,F)),
list(title = "Daily SO2 AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr"))),
list(label = "co",
method = "update",
args = list(list(visible = c(F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F, F,F, T,T)),
list(title = "Daily CO AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr")))
))
))This interactive plot shows each pollutant’s Daily AQI Distribution, 2019 and 2020 Feb-Apr, in each city. The users can click on the dropdown selection button on the top left to choose the pollutant type: PM2.5, PM10, O3, NO2, SO2 and CO. Each city has two boxes. The blue one represents the 2020 Feb-Apr period, and the red one represents the 2021 Feb-Apr period. Besides, the median, min, max, q1, q3 and outliers are showed in the box plot for each city. This plot indicates that the distributions of daily pollutant AQI in 2020 (blue) are generally lower than those in 2019 (red).
Line charts of daily pm2.5 AQI for 30 major cities.
(Note that year 2019 does not have the date “Feb 29”, but year 2020 does.)
city_AQI_Distribution %>%
ggplot(aes(x = day, y = pm25, color = period)) +
geom_line(aes(group = period), size = 0.8) +
#geom_point() +
scale_color_hue(direction = -1) +
ylim(0, 400) +
labs(
title = "Daily PM25 AQI Starting From Feb 1 to Apr 30",
x = "Day",
y = "Daily PM25 AQI",
color = "year period") +
facet_wrap(~city, nrow = 10) +
scale_x_discrete(breaks = c("02-01", "02-11", "02-21",
"03-01", "03-11", "03-21",
"04-01", "04-11", "04-21")) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1)) 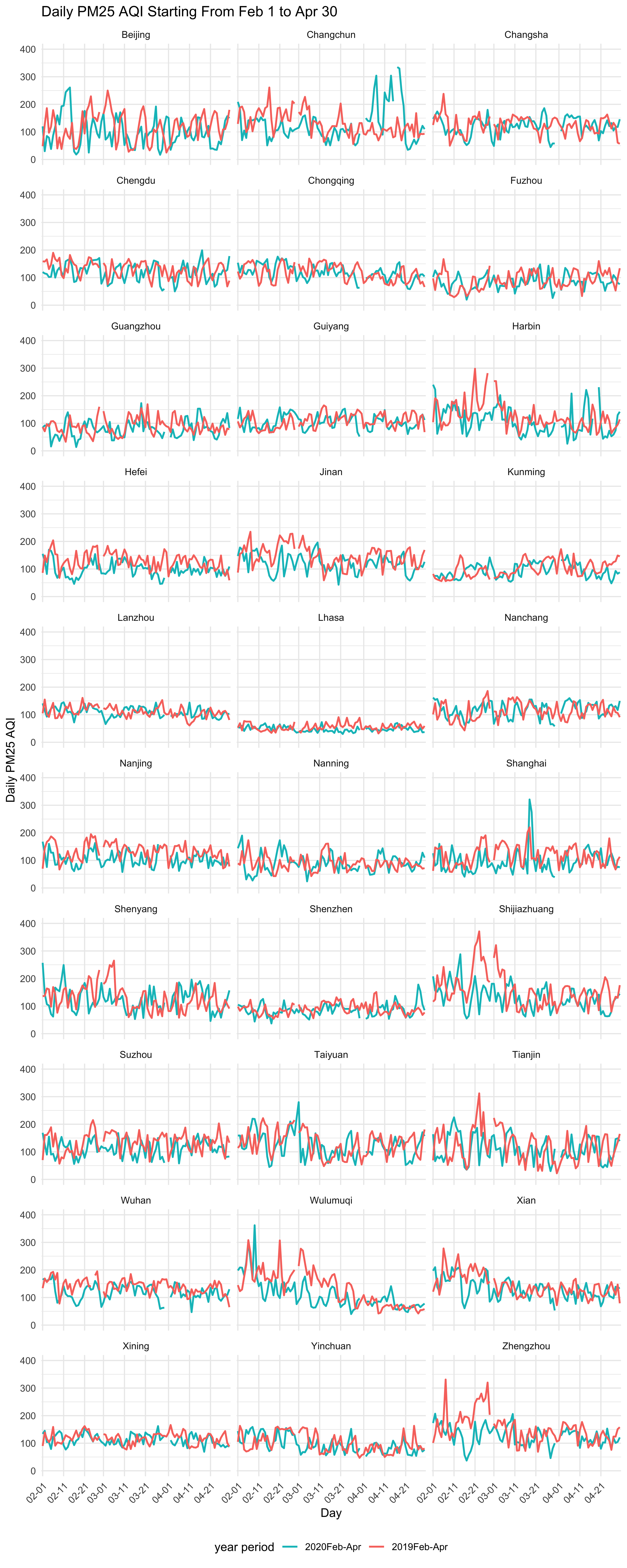
These line charts show daily PM2.5 AQI starting from Feb1 to Apr 30. For each city, the blue line represents data from 2020, and red line represents data from 2019. Thus in the graphs, the red lines of year 2019 does not have data for Feb 29, but the blue lines of year 2020 do.
We can see that although there are fluctuations, generally daily PM2.5 AQI during the lockdown is lower than the same period in year 2019, for each city. Besides, some cities such as Beijing, Changchun, Harbin, Shanghai, Shijiazhuang, Tianjin, Yinchuan and Zhengzhou have violent fluctuations compared to other cities. This can be explained that most of them are located in the North of China. That is partly because the north cities need more fuels to housing supply and heavy industry.
Line charts of daily NO2 AQI changes for all 30 cities.
city_AQI_Distribution %>%
ggplot(aes(x = day, y = no2, color = period)) +
geom_line(aes(group = period), size = 0.8) +
#geom_point() +
scale_color_hue(direction = -1) +
ylim(0, 60) +
labs(
title = "Daily NO2 AQI Starting From Feb 1 to Apr 30",
x = "Day",
y = "Daily NO2 AQI",
color = "year period") +
facet_wrap(~city, nrow = 10) +
scale_x_discrete(breaks = c("02-01", "02-11", "02-21",
"03-01", "03-11", "03-21",
"04-01", "04-11", "04-21")) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1)) 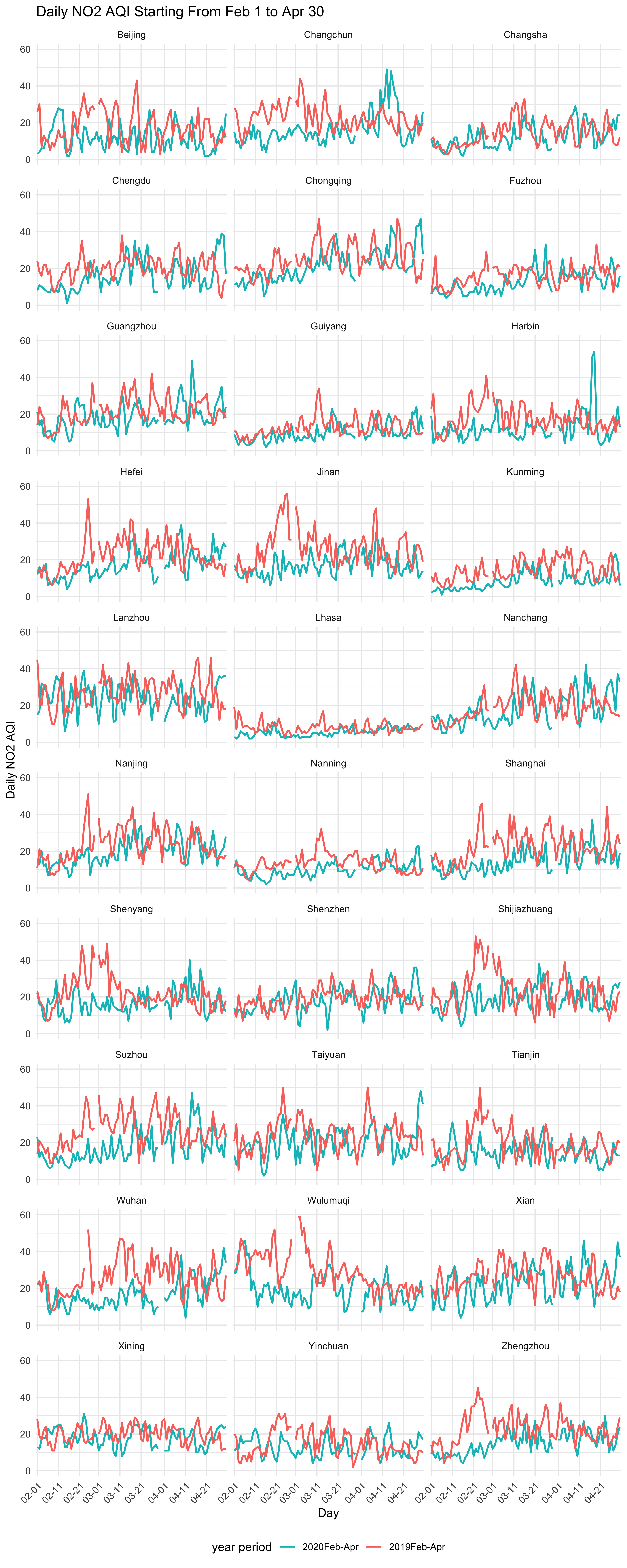
These line charts show daily NO2 AQI starting from Feb 1 to Apr 30. Similar to PM2.5 AQI trends, daily NO2 AQI during the lockdown is generally lower than the same period in year 2019 for each city. In addition, daily NO2 AQI of most cities have more violent fluctuations than daily PM2.5 AQI. Only Nanning and Shenzhen have relatively weaker fluctuations among 30 cities.
Past Four Years’ Feb~Apr Mean PM2.5 AQI
A bar graph of mean PM2.5 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years in 30 representative cities.
for (city_file in city_files) {
#print(city_file)
path = str_c("30_cities_data/", city_file)
city = strsplit(city_file, split = '-')[[1]][1]
cityAir = read_csv(path) %>%
mutate(date = as.Date(date, "%Y/%m/%d")) %>%
arrange(date)
cityAir_18 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_18)
cityAir_19 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_19)
cityAir_20 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_20)
cityAir_21 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_21)
mean_18 = mean(cityAir_18$pm25, na.rm = T)
mean_19 = mean(cityAir_19$pm25, na.rm = T)
mean_20 = mean(cityAir_20$pm25, na.rm = T)
mean_21 = mean(cityAir_21$pm25, na.rm = T)
city_4year_meanPM25 =
city_4year_meanPM25 %>%
add_row(city = city,
mean_18 = mean_18,
mean_19 = mean_19,
mean_20 = mean_20,
mean_21 = mean_21)
}city_4year_meanPM25 =
city_4year_meanPM25 %>%
mutate(city = factor(city)) %>%
pivot_longer(
mean_18:mean_21,
values_to = "mean",
names_to = "years"
)city_4year_meanPM25 %>%
ggplot() +
geom_bar(
aes(y = years, x = mean, fill = years),
stat = "identity") +
facet_wrap(~city, nrow = 5) +
#scale_x_continuous(breaks = scales::pretty_breaks(n = 20)) +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(
title = "A bar graph of mean PM2.5 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years",
x = "PM25 AQI Mean",
y = "City")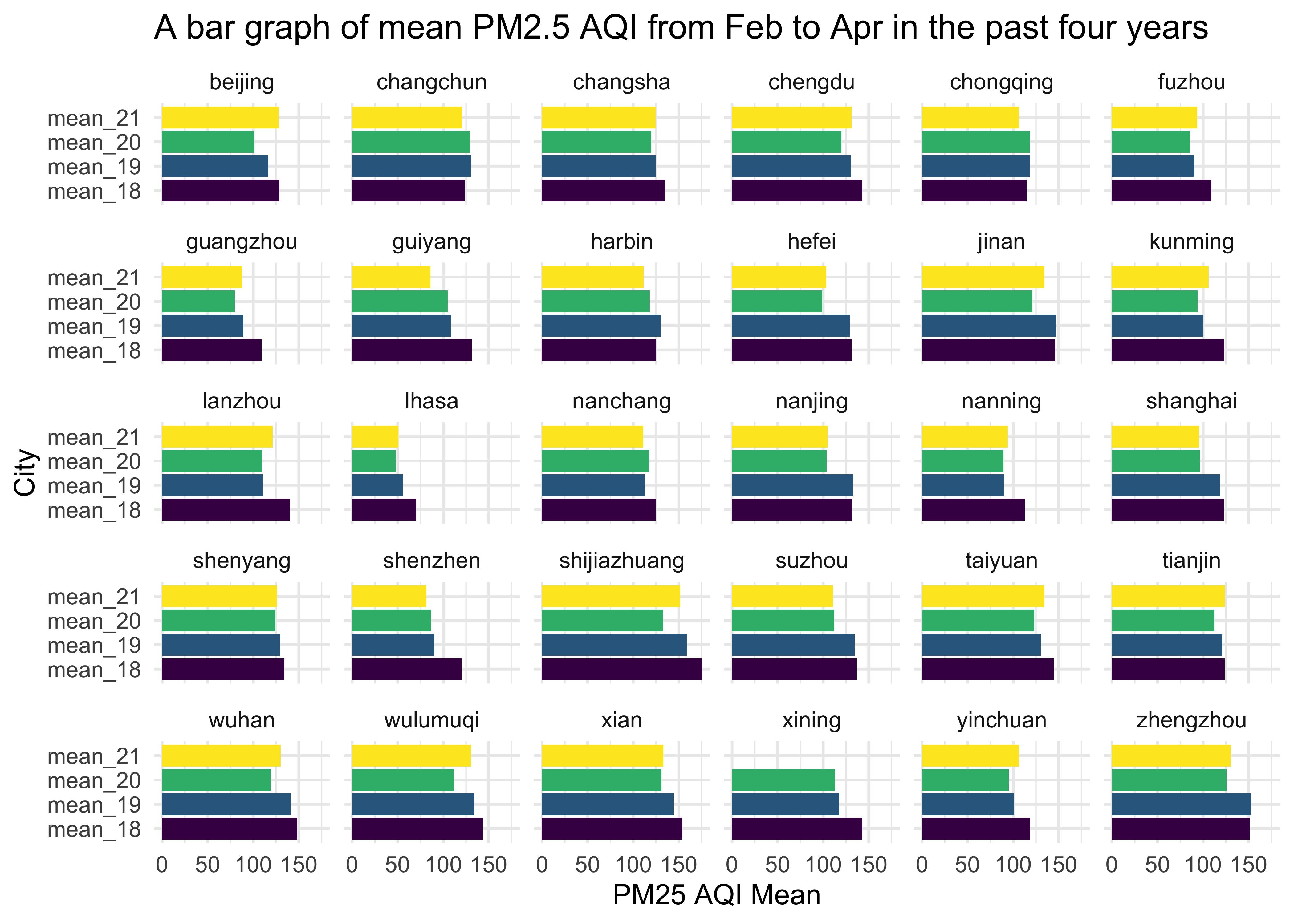
This bar graph shows mean PM2.5 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years for 30 cities. (note Xining does not have mean of 2021.) We can see the trend that mean PM2.5 AQI decreased from 2018 to 2020 but bounced back in 2021 for most of 30 cities. The mean PM2.5 AQI in 2020 is the lowest one compared with other 3 years. This is highly likely to be due to the lockdown policy in 2020. The mean PM2.5 AQI in 2021 gets back up because of the economy recovery.
Past Four Years’ Feb~Apr Mean NO2 AQI
A bar graph of mean NO2 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years in 30 representative cities.
city_4year_meanno2 =
tibble(city = character(),
mean_18 = numeric(),
mean_19 = numeric(),
mean_20 = numeric(),
mean_21 = numeric())for (city_file in city_files) {
#print(city_file)
path = str_c("30_cities_data/", city_file)
city = strsplit(city_file, split = '-')[[1]][1]
cityAir = read_csv(path) %>%
mutate(date = as.Date(date, "%Y/%m/%d")) %>%
arrange(date)
cityAir_18 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_18)
cityAir_19 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_19)
cityAir_20 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_20)
cityAir_21 = cityAir %>%
filter(date %within% period_21)
mean_18 = mean(cityAir_18$no2, na.rm = T)
mean_19 = mean(cityAir_19$no2, na.rm = T)
mean_20 = mean(cityAir_20$no2, na.rm = T)
mean_21 = mean(cityAir_21$no2, na.rm = T)
city_4year_meanno2 =
city_4year_meanno2 %>%
add_row(city = city,
mean_18 = mean_18,
mean_19 = mean_19,
mean_20 = mean_20,
mean_21 = mean_21)
}city_4year_meanno2 =
city_4year_meanno2 %>%
mutate(city = factor(city)) %>%
pivot_longer(
mean_18:mean_21,
values_to = "mean",
names_to = "years"
)city_4year_meanno2 %>%
ggplot() +
geom_bar(
aes(y = years, x = mean, fill = years),
stat = "identity") +
facet_wrap(~city, nrow = 5) +
#scale_x_continuous(breaks = scales::pretty_breaks(n = 20)) +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(
title = "A bar graph of mean NO2 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years",
x = "NO2 AQI Mean",
y = "City")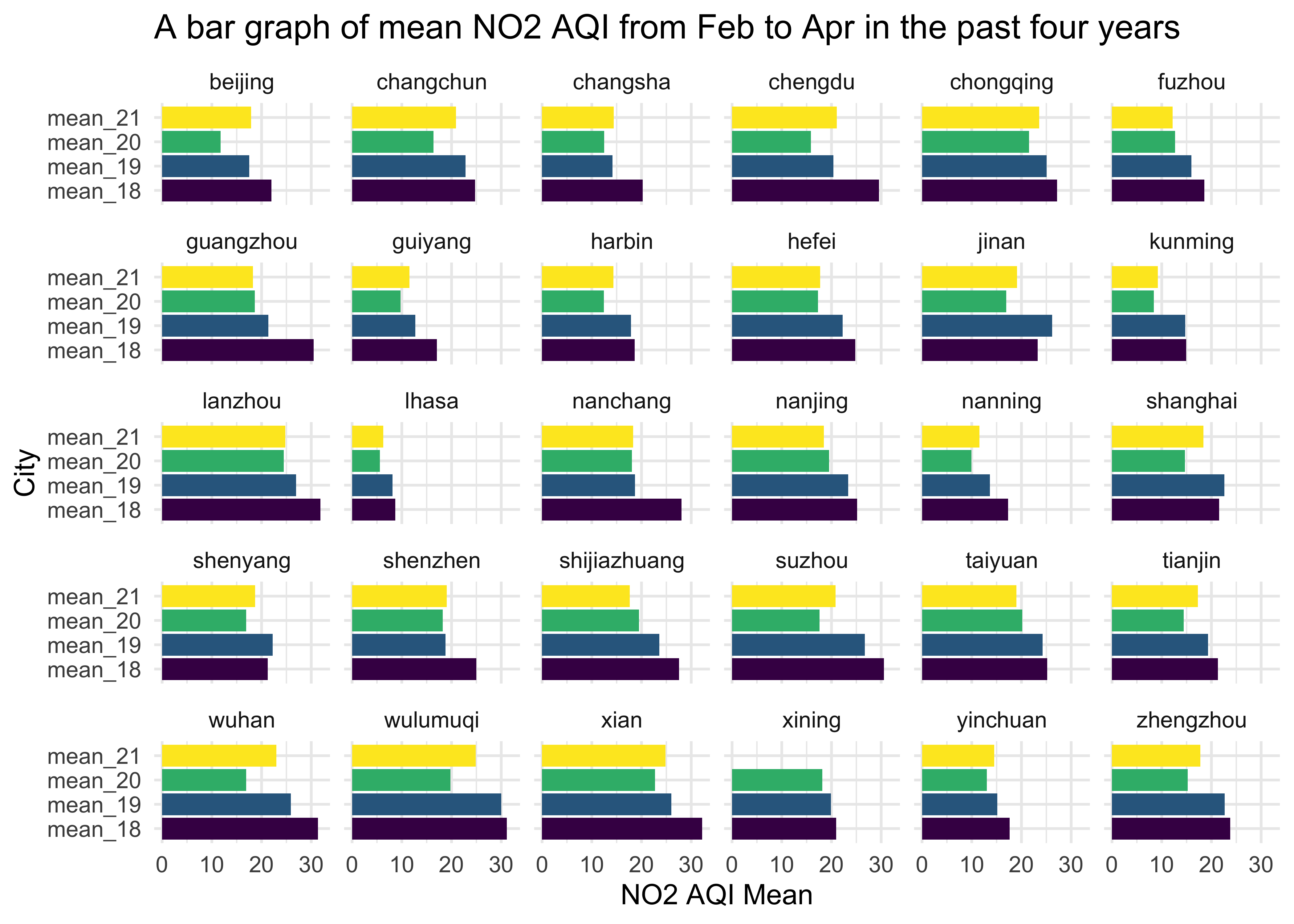
This bar graph shows mean NO2 AQI from Feb to Apr in the past four years for 30 cities. (note Xining does not have mean of 2021.) Mean NO2 AQI has similar trends to mean PM2.5 AQI. And the reason for this trend is the same as PM2.5 AQI.